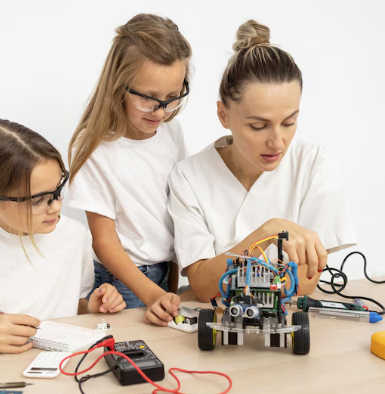
Robotics is reshaping education by introducing students to problem-solving, creativity, and technical skills through hands-on learning experiences. As industries increasingly adopt automation and intelligent systems, integrating robotics into the classroom equips the next generation with essential skills for the future. From elementary schools to universities, robotics education fosters critical thinking and inspires interest in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) careers.
1. Why Robotics Matters in Education
Robotics brings abstract concepts to life. Students don’t just learn theory—they build, program, and test robots that respond to real-world challenges. This active approach enhances engagement and reinforces knowledge retention across subjects, especially math, physics, and computer science.
2. Introducing Robotics at an Early Age
Elementary students can start learning robotics using age-appropriate kits like LEGO Education SPIKE or VEX GO. These platforms use visual programming languages to teach basic logic and sequencing, helping young learners build confidence and develop a growth mindset through experimentation.
3. Middle and High School Integration
In middle and high school, robotics becomes more advanced, incorporating coding skills, sensors, motors, and control systems. Programs such as FIRST Robotics, Arduino projects, and micro:bit activities allow students to engage in team-based challenges that promote collaboration, leadership, and perseverance.
4. Robotics and Interdisciplinary Learning
Robotics supports cross-curricular learning. A robotics project might include elements of math (geometry and measurement), science (forces and energy), engineering (design and prototyping), and art (aesthetics and user interface). This blend of disciplines encourages innovation and holistic thinking.
5. Supporting Equity and Inclusion
Robotics programs can help bridge the digital divide by providing all students with access to hands-on technology. Inclusive robotics education empowers underrepresented groups—especially girls and minorities—to pursue STEM careers by cultivating early interest and confidence.
6. Robotics in Higher Education and Career Pathways
Colleges and universities offer specialized robotics courses that prepare students for careers in automation, artificial intelligence, and engineering. Students learn to design autonomous systems, simulate robotic behavior, and apply robotics to industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and space exploration.
7. Teacher Training and Classroom Resources
Effective robotics instruction requires teacher support and professional development. Many organizations offer educator training, curriculum guides, and online communities to help teachers integrate robotics into their classrooms. Resources like RoboBlockly, CS-STEM Network, and CoderZ provide turnkey lessons and platforms.
8. The Future of Robotics in Education
As robotics technology evolves, future classrooms may feature AI-enhanced learning robots, virtual simulators, and collaborative programming environments. Robotics will continue to foster digital literacy, problem-solving, and innovation, making it a cornerstone of modern education.
Conclusion
Robotics in education goes beyond machines—it cultivates curiosity, creativity, and future-ready skills. By integrating robotics into classrooms at every level, educators can inspire students to explore new technologies, think critically, and prepare for tomorrow’s challenges. Whether building simple bots or designing complex systems, students are learning to shape the future with their own hands.